Ear infections can affect different parts of the ear and vary in severity. The main types of ear infections are:
Types of Ear Infections:
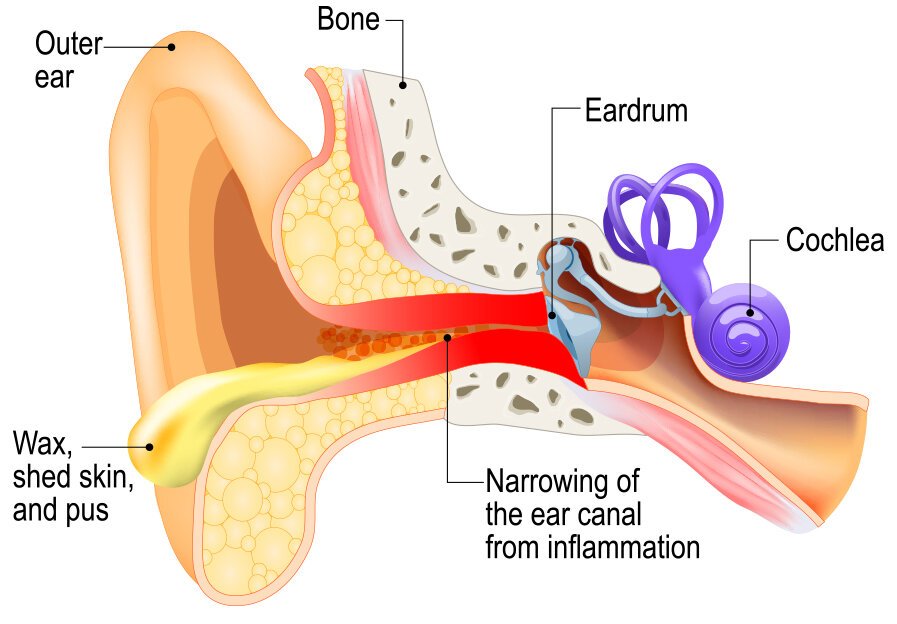
- Otitis Externa (Outer Ear Infection):
- Cause: Infection of the ear canal, often referred to as “swimmer’s ear.” It can be caused by bacteria, fungi, or irritants such as water exposure or chemicals.
- Symptoms: Itching, redness, discharge, pain, and sometimes swelling of the ear canal. The ear may feel blocked or have a sensation of fullness.
- Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection):
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM):
- Cause: Infection of the middle ear, often following a cold or respiratory infection. It is commonly caused by bacteria or viruses.
- Symptoms: Ear pain, fever, irritability in children, hearing loss, and fluid drainage if the eardrum ruptures.
- Otitis Media with Effusion (OME):
- Cause: Fluid accumulation in the middle ear without an active infection, often following an acute infection or due to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Symptoms: Hearing loss, a feeling of fullness in the ear, and sometimes mild discomfort. It may not be associated with pain or fever.
- Chronic Otitis Media:
- Cause: Persistent or recurrent infections that lead to long-term inflammation and damage to the middle ear and eardrum.
- Symptoms: Persistent ear discharge, hearing loss, and possible pain and discomfort.
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM):
- Otitis Interna (Inner Ear Infection):
- Cause: Infection of the inner ear structures, such as the cochlea or vestibular apparatus. It is less common and can be associated with viral infections or conditions like labyrinthitis.
- Symptoms: Severe vertigo (dizziness), hearing loss, nausea, and sometimes tinnitus.
Causes of Ear Infections:
- Bacterial Infections: Common bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis.
- Viral Infections: Viruses such as those causing the common cold or flu can lead to secondary ear infections.
- Fungal Infections: Can occur in the outer ear canal, especially in moist environments.
- Allergies: Can cause inflammation and fluid buildup, contributing to infections.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Blockage or improper function of the Eustachian tube can lead to fluid accumulation and infections.
- Water Exposure: Prolonged exposure to water can lead to infections in the outer ear.
Symptoms:
- Outer Ear Infection (Otitis Externa):
- Itching or pain in the ear canal.
- Redness and swelling of the ear canal.
- Discharge or drainage from the ear.
- Feeling of fullness or blockage in the ear.
- Middle Ear Infection (Otitis Media):
- Ear pain or discomfort.
- Fever (especially in children).
- Hearing loss or muffled hearing.
- Fluid drainage if the eardrum ruptures.
- Irritability or difficulty sleeping in children.
- Inner Ear Infection (Otitis Interna):
- Severe vertigo or dizziness.
- Hearing loss.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears).
Diagnosis:
- Medical History and Physical Examination:
- Discussing symptoms, their onset, and any recent illnesses or exposures.
- Otoscopy:
- Examining the ear canal and eardrum to identify signs of infection or fluid buildup.
- Hearing Tests:
- Audiometry: To assess hearing loss and evaluate the impact on auditory function.
- Additional Tests:
- Tympanometry: To evaluate the function of the middle ear and eardrum.
- Cultures: To identify the causative bacteria or fungi in cases of persistent or severe infections.
- Imaging:
- CT or MRI Scans: In rare cases, to rule out complications or structural abnormalities.
Homeopathy for Ear Infections:
Some homeopathic remedies that might be considered include:
- Calendula: For infections with inflammation and discharge.
- Belladonna: For sudden onset of ear pain with redness and sensitivity.
- Pulsatilla: For ear infections with thick, yellow discharge and a tendency for symptoms to change frequently.
- Hepar Sulph: For infections with intense pain and sensitivity to touch.

