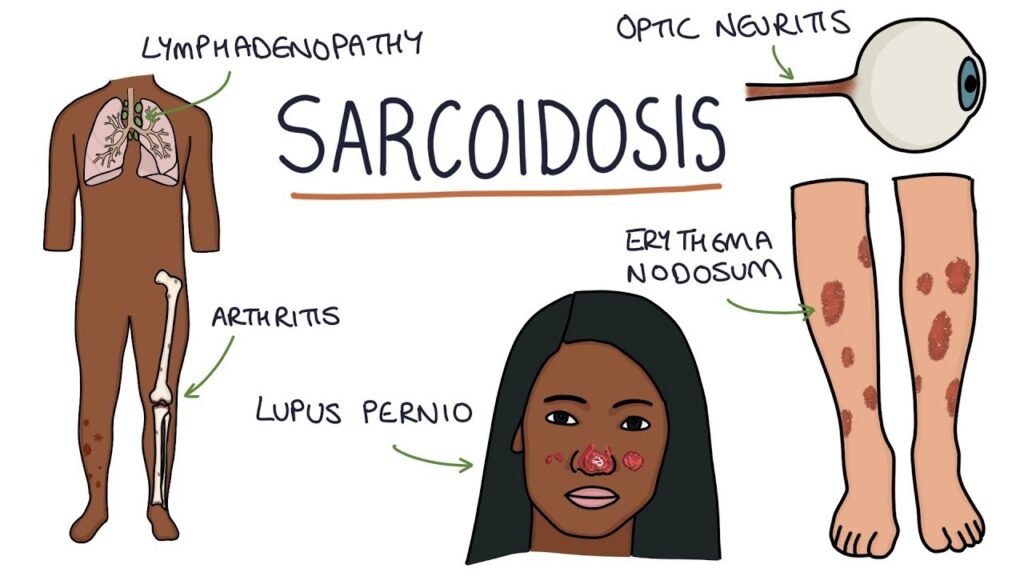
Sarcoidosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of granulomas—small clusters of inflammatory cells—in various organs. The exact cause is unknown, but it most commonly affects the lungs and lymph nodes and can involve other organs such as the skin, eyes, and liver.
Causes:
The exact cause of sarcoidosis is not known, but several factors may contribute:
- Immune System Response: It is thought to be related to an abnormal immune response, possibly triggered by infections, environmental factors, or genetic predisposition.
- Genetic Factors: Family history of sarcoidosis or other autoimmune diseases might increase the risk.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain substances, such as silica dust or mold, might play a role in some cases.
Symptoms:
Symptoms can vary depending on which organs are affected:
- Lung Involvement:
- Persistent Cough: A chronic, dry cough.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or breathlessness.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest.
- Lymph Node Involvement:
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Typically in the chest, neck, or underarms.
- Skin Involvement:
- Rashes: Red or purple bumps (nodules) on the skin, often on the legs or arms.
- Skin Changes: Darkening or lightening of skin patches.
- Eye Involvement:
- Uveitis: Inflammation of the uvea (middle layer of the eye), leading to symptoms such as redness, pain, and vision problems.
- Other Organ Involvement:
- Liver: Enlargement or dysfunction.
- Spleen: Enlargement or other issues.
Diagnosis:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Assessment of symptoms and examination of affected areas.
- Imaging Studies:
- Chest X-ray: To check for lung involvement and lymph node enlargement.
- CT Scan: Provides a more detailed view of affected organs.
- Biopsy:
- Granuloma Biopsy: Tissue samples from affected organs (e.g., lungs, skin) to identify granulomas.
- Blood Tests:
- Serum Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE): Elevated levels can be indicative of sarcoidosis, though not specific.
Homeopathy for Sarcoidosis:
Homeopathy can be used to support overall health and manage symptoms in conjunction with conventional treatment. It is important to work with a qualified homeopathic practitioner to choose remedies based on individual symptoms and overall health.
Some homeopathic remedies that might be considered include:
- Calcarea Carbonica: For chronic fatigue, weakness, and overall sluggishness, especially if there are also skin or respiratory symptoms.
- Silica: For supporting the body’s healing process and addressing issues related to chronic conditions.
- Arsenicum Album: For symptoms of fatigue, weakness, and respiratory issues, often with a feeling of restlessness or anxiety.
- Hepar Sulphuris: For inflammation with sensitivity and suppuration (pus formation).

