Lymphatic filariasis, also known as lymphatic elephantiasis, is a parasitic disease caused by thread-like worms belonging to the Filarioidea family. The disease is transmitted through mosquito bites and affects the lymphatic system, leading to severe complications.
Causes and Transmission:
- Parasites:
- Wuchereria bancrofti: The most common cause of lymphatic filariasis.
- Brugia malayi and Brugia timori: Other filarial species responsible for the disease.
- Transmission:
- The disease is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito, which carries the filarial larvae (microfilariae) that enter the bloodstream and migrate to the lymphatic system.
Symptoms:
Lymphatic filariasis can present in several forms, including:
- Acute Stage:
- Filarial Fever: Recurrent fever episodes, often accompanied by pain and swelling.
- Lymphangitis: Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels, leading to redness, pain, and swelling.
- Chronic Stage:
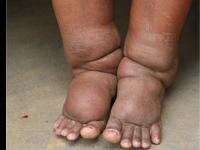
- Lymphedema: Severe swelling of the limbs, usually the legs, and sometimes the arms or genitals.
- Elephantiasis: Thickening and hardening of the skin, leading to a characteristic appearance of the affected body parts.
- Hydrocele: Swelling of the scrotum due to fluid accumulation, common in men.
Diagnosis:
- Microscopy:
- Blood Smear: Detection of microfilariae in the blood, usually done at night when the larvae are more likely to be present in the bloodstream.
- Serological Tests:
- Antibody or Antigen Tests: To detect the presence of specific antibodies or antigens related to filarial infection.
- Imaging:
- Ultrasound: To assess lymphatic damage and associated complications.
- Biopsy:
- In some cases, tissue biopsy might be done to confirm the presence of adult worms or other parasitic forms.
Homoeopathy Treatment:
While homeopathy is not a substitute for conventional antiparasitic treatment, some remedies may be used to support overall health and manage symptoms:
- Calcarea Carbonica: For chronic swelling and general weakness.
- Lachesis: For symptoms of constriction and discomfort in swollen limbs.
- Apis Mellifica: For acute swelling with a burning sensation, particularly if the swelling is painful and sensitive.
- Rhus Toxicodendron: For discomfort and stiffness in swollen limbs, especially if symptoms improve with movement.

